Arcfra Distributed Storage vs. VMware vSAN: Comparable Features, Optimized Performance, and Stability
As enterprises evaluate VMware alternatives, storage capabilities — across both block and file workloads — become a critical point of comparison. As a Gartner-recognized sample VMware alternative, Arcfra Enterprise Cloud Platform (AECP) incorporates Arcfra Block Storage (ABS) and Arcfra File Storage (AFS), delivering enterprise-grade capabilities, reliability, security, and operational simplicity on par with VMware vSAN. Moreover, with optimized features such as volume pinning and I/O localization, AECP can achieve superior performance and stability than vSAN.
Key Feature Comparisons
As AECP’s storage components, ABS and AFS provide distributed block and file storage services for mission-critical applications running on VMs, containers, and physical machines. They support hyperconverged deployment with Arcfra Virtualization Engine (AVE) or VMware ESXi to support diverse application scenarios.
Particularly, with ABS and AFS, AECP has matched and even exceeded vSAN across storage reliability, performance, security, protocol support, storage policies, space efficiency, and cloud-native storage support. This means that AECP enables users to configure storage with greater flexibility, fulfill diverse business requirements, and ensure highly reliable, high-performance access across different use cases. A detailed feature comparison is provided below.
| Feature | VMware vSAN | Arcfra ABS and AFS |
| 1. Reliability | ||
| Data Redundancy Strategies | ✅ RAID 1 (2/3/4 replicas), RAID 5 (EC 3+1), RAID 6 (EC 4+2) | ✅ 2/3 replicas 28 combinations of EC K+M M=1 or 2, K=2~22 (even) M=3 or 4, K=4~8 (even) |
| Rack Topology Awareness | ✅ | ✅ |
| Active-active Cluster | ✅ | ✅ |
| Silent Data Corruption Detection | ✅ Checksum | ✅ Checksum & data inspection |
| Disk Health Check | ✅ | ✅ |
| Network Health Check | ❌ Only basic network monitoring | ✅ Automatic isolation of anomaly NICs or nodes |
| 2. Performance | ||
| File Controller HA | ✅ | ✅ HA for file access IPs to ensure business continuity |
| Hot/Cold Data Tiering | ✅ | ✅ Cache acceleration with intelligent hot/cold data tiering |
| Volume Pinning | ❌ Only reserve read cache; cannot prevent data sinking | ✅ Reserve write cache; prevent data sinking to ensure performance |
| High Speed Data Transfer Protocol | ✅ RDMA | ✅ RDMA |
| I/O Localization | ❌ Partial I/O localization | ✅ Prioritize local I/O |
| Intelligent Data Recovery | ✅ | ✅ Dynamically adjust recovery speed to prioritize business I/O |
| File System Multi-Path Mounting | ❌ Access only via a single assigned IP, or redirected from the primary IP to an internal assigned IP | ✅ Support mounting file systems through multiple access IP paths |
| 3. Security | ||
| Snapshot | ✅ Snapshot, snapshot scheduling | ✅ Snapshot, snapshot scheduling |
| Data Encryption | ✅ Data-at-rest & data-in-transit encryption | ✅ Support Data-in-transit encryption as well for vMotion traffic etc |
| File System Accessibility | ❌ File systems cannot be taken offline/online | ✅ Manageable via online/offline operations on the server side |
| 4. Supported Protocols | ||
| VM | ✅ Object | ✅ iSCSI/vhost |
| Block Storage | ✅ iSCSI | ✅ iSCSI/NVMe over TCP/NVMe over RDMA |
| File Storage | ✅ NFS/SMB | ✅ NFS/HDFS |
| 5. Storage Policies | ||
| QoS | ✅ Only support IOPS limit settings | ✅ Support IOPS/bandwidth limit settings and allow for I/O Bursting |
| Multi-policy Per Pool | ✅ Volume-level | ✅ Volume-level |
| 6. Space Efficiency | ||
| Space Reclamation | ✅ | ✅ |
| Deduplication & Compression | ✅ | ❌ |
| 7. Cloud-Native Storage | ||
| CSI Driver | ✅ vSphere Container Storage Plug-in (Block & File) | ✅ Arcfra ABS CSI Driver (Block) Kubernetes NFS CSI Driver |
Disk Architecture, Configuration Requirements, and Limitations
Compared with VMware vSAN, Arcfra ABS & AFS offer more flexible disk configuration options. It supports online expansion of both cache and capacity disks without service impact, and automatically adjusts capacity-balancing strategies based on utilization. This leads to a more elastic storage architecture and a more simplified O&M experience.
| Item | VMware | Arcfra |
| Disk Architecture | OSA: - Number of disk groups per node: >=2 - Disk group composition: 1 SSD + 1~7 HDD or 1 SSD + 1~7 SSD - All-flash only supported in tiered mode - Cache disks do not support redundancy - A single cache disk failure causes the entire disk group to go offline, leading to a large data rebuild volume and reduced usable capacity ESA: All-flash only, requires at least 4 NVMe SSDs per host | All-flash supports both tiered and non-tiered modes (requires ≥ 2 NVMe/SATA SSDs) Cache disks support redundancy A single cache disk failure does not cause HDDs to go offline; Usable capacity remains unchanged, with minimal data rebuild |
| Expansion of Capacity Disks | OSA: A disk group supports up to 7 capacity disks. e.g., if a node has 14 HDDs across 2 disk groups and you add 2 more HDDs, you must create a new disk group and add a new cache disk. The number of disks added must scale with node count × disk group count. For a 3-node cluster with 2 disk groups per node, each expansion requires adding at least 6 disks. ESA: Supports single-disk expansion. | Cache is globally shared; cache disk quantity does not depend on HDD count. Supports online expansion of capacity disks, allowing different capacities and quantities to be added per node. |
| Expansion of Cache Disks | OSA: To expand cache capacity, the entire disk group must be taken offline and replaced with a larger-capacity SSD, or the disk group must be split and rebuilt after adding a new cache disk. Both approaches require pre-clearing all data in the disk group, resulting in a long preparation time. If the cache disk is replaced directly, data must be rebuilt from replicas, during which redundancy levels are reduced, creating data-safety risks. The maximum write-cache capacity is 1.6 TB. As data volume grows, cache exhaustion occurs easily, causing significant performance degradation. ESA: ESA has no dedicated cache disk. | Supports online expansion of cache disks without impacting existing disks or data and without affecting running workloads. A single node supports up to 25 TB of cache, making cache exhaustion unlikely. Resident caching further keeps data in cache to avoid cache exhaustion. |
| Capacity Balancing Strategy | OSA: With default settings, load balancing begins when any storage device reaches 80% utilization, often causing significant performance jitter. VMware recommends keeping utilization below 70%. ESA: No fixed threshold; performance impact is small. | With default settings, different load-balancing strategies are applied at low, medium, and high storage-utilization levels to ensure timely and stable balancing. Even at high utilization (above 85%), performance remains stable. |
Snapshot Mechanism Comparisons
Compared with VMware vSAN, ABS employs a metadata-based snapshot mechanism that combines Redirect-On-Write (ROW) and Copy-On-Write (COW). Only metadata is copied during snapshot creation, enabling snapshot operations within seconds. Snapshots are independent of one another, allowing deletion at any time without merge operations or performance degradation.
| Item | VMware vSAN (OSA) | Arcfra ABS |
| Snapshot Mechanism | Redo-log-based snapshots require redirect-on-write. Need to traverse various files for VM read/write. Apparent performance impact when snapshot. | Metadata snapshot, metadata stored centrally. No need for a full-scale query for VM read/write. Minimum performance impact when snapshot. |
| Snapshot Execution | Performance degradation is long-term unless snapshot deletion. | Short-term performance degradation after snapshots, and will resume afterwards. |
| Snapshot Deletion | Performance degradation is huge (80%+). Snapshot deletion can sometimes cost hours. | No performance impact after snapshot deletion. Deletion can be done very quickly. |
Performance Comparisons
We conducted a series of real-world tests to compare the performance of Arcfra ABS and VMware vSAN. The test environment used Arcfra Cloud Operating System (ACOS) 6.2 and vSAN 8.0, both integrated with VMware ESXi 8.0. The test items included:
- Performance under snapshot creation
- Performance under high capacity utilization
- Performance under failure scenarios
- Long-term performance and stability under Oracle databases
| Hardware Item | Configuration Details |
| CPU | 2 x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5218R CPU @ 2.10GHz |
| Memory | 256GB |
| Cache Disk | INTEL SSDPF2KE016T1O NVMe SSD x 2 |
| Capacity Disk | 8TB x 4 |
| Storage NIC | Mellanox Technologies MT27800 Family [ConnectX-5] 25GbE x 1 |
Performance under Snapshot Creation
Hybrid-Flash Cluster
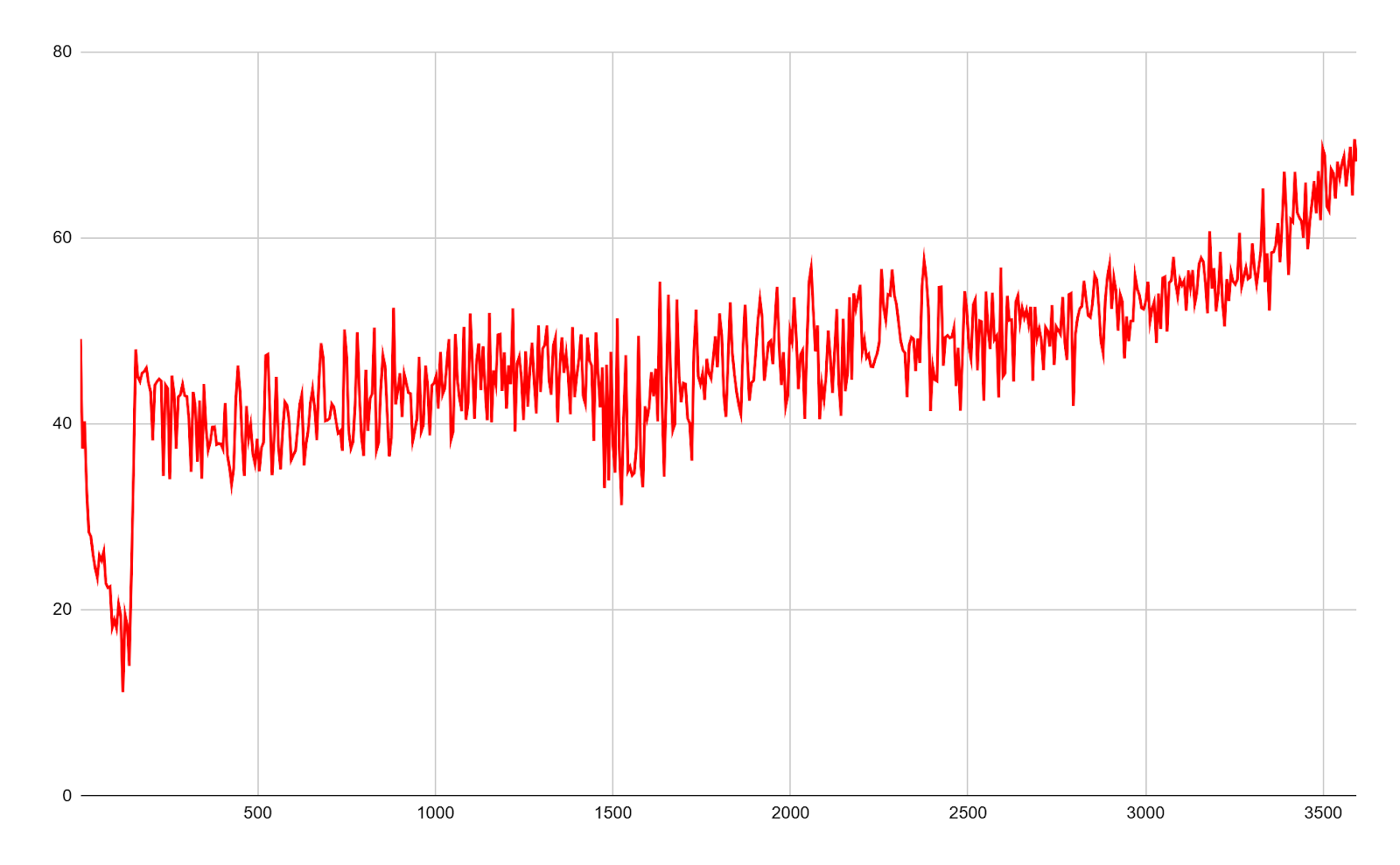
After snapshot creation, vSAN OSA experienced a significant and long-lasting performance drop accompanied by severe jitter. In contrast, Arcfra ACOS showed only a momentary performance dip at the instant of snapshot creation and quickly returned to normal performance with minimal jitter.
Impact of Snapshot Creation on 4K Random Write Performance (Hybrid-Flash Cluster)
Arcfra ACOS 6.2
vSAN 8.0 OSA
All-Flash Cluster
Both Arcfra ACOS and vSAN experienced a momentary performance drop during snapshot creation, followed by a rapid return to normal performance levels. However, vSAN ESA performed noticeably better than OSA after snapshots but still showed a certain degree of jitter, whereas Arcfra ACOS exhibited minimal jitter and maintained stable performance.
Impact of Snapshot Creation on 4K Random Write Performance (All-Flash Cluster)
.png)
Arcfra ACOS 6.2 (with RDMA enabled)
vSAN 8.0 ESA
Learn more about the key features of ABS from our previous blog: Arcfra vs. VMware: VM Snapshot and I/O Performance Comparison.
Performance under High Capacity Utilization
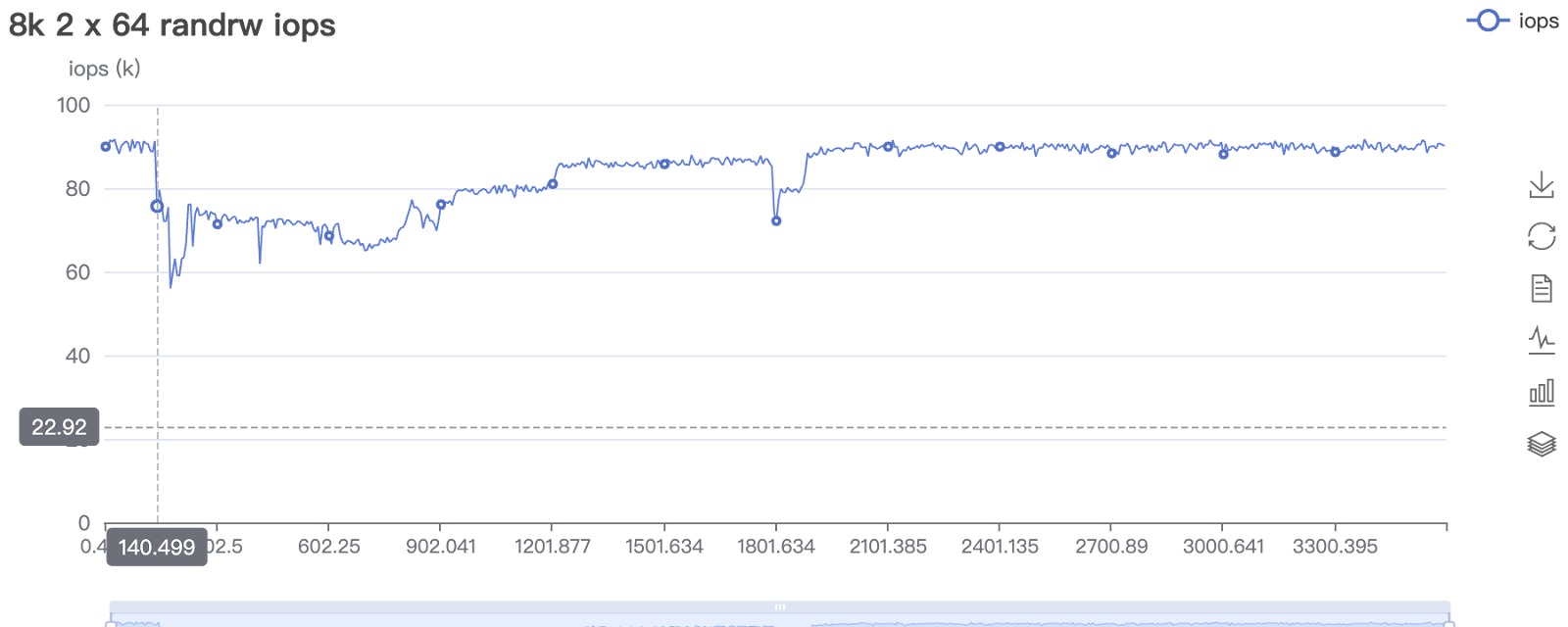
Under high storage utilization, vSAN 8.0 exhibited a significant drop in 4K random write performance along with severe jitter. In contrast, Arcfra ACOS maintained more stable and superior 4K random write performance under the same high-utilization conditions.
4K Random Write IOPS Comparison at 80% Cluster Storage Utilization
Performance under Failure Scenarios
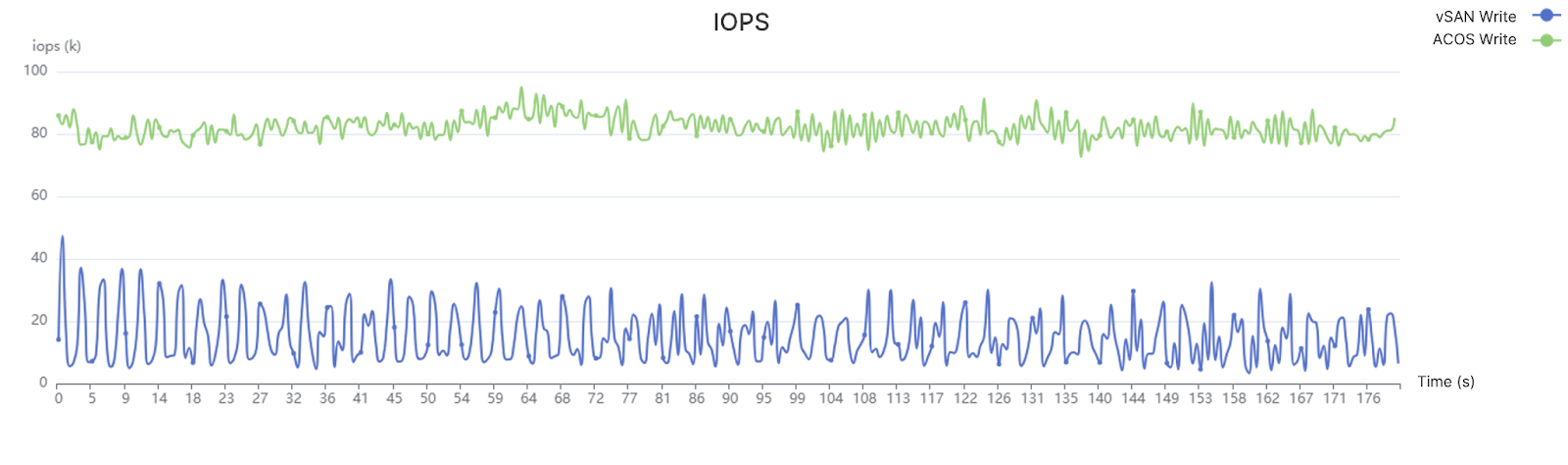
Under a host failure, ACOS clusters experienced only a slight performance degradation on VMs running on healthy nodes, and performance returned to normal within a short period, maintaining overall stability. In contrast, VMware vSAN experienced a much larger and longer-lasting performance degradation on healthy nodes, and in some cases, temporary I/O even dropped to zero.
ACOS 6.2
.png)
vSAN 8.0 OSA
Under a storage network failure, ACOS clusters automatically triggered I/O rerouting, while vSAN triggered HA. Due to the I/O rerouting process, VM performance on ACOS’ healthy nodes experienced a noticeable performance drop, but overall performance remained stable. In contrast, VMware vSAN experienced a much greater performance decrease on healthy nodes, with performance dropping by up to 70% and remaining degraded for an extended period.
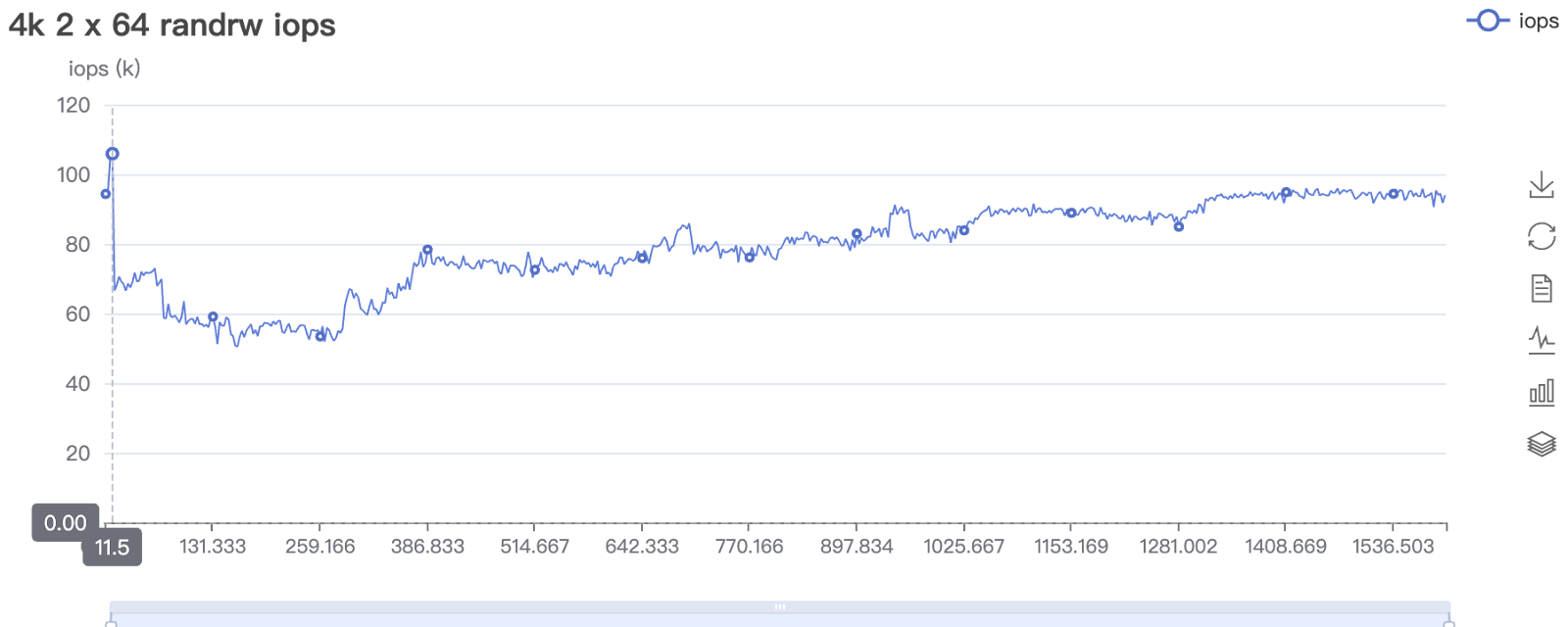
ACOS 6.2
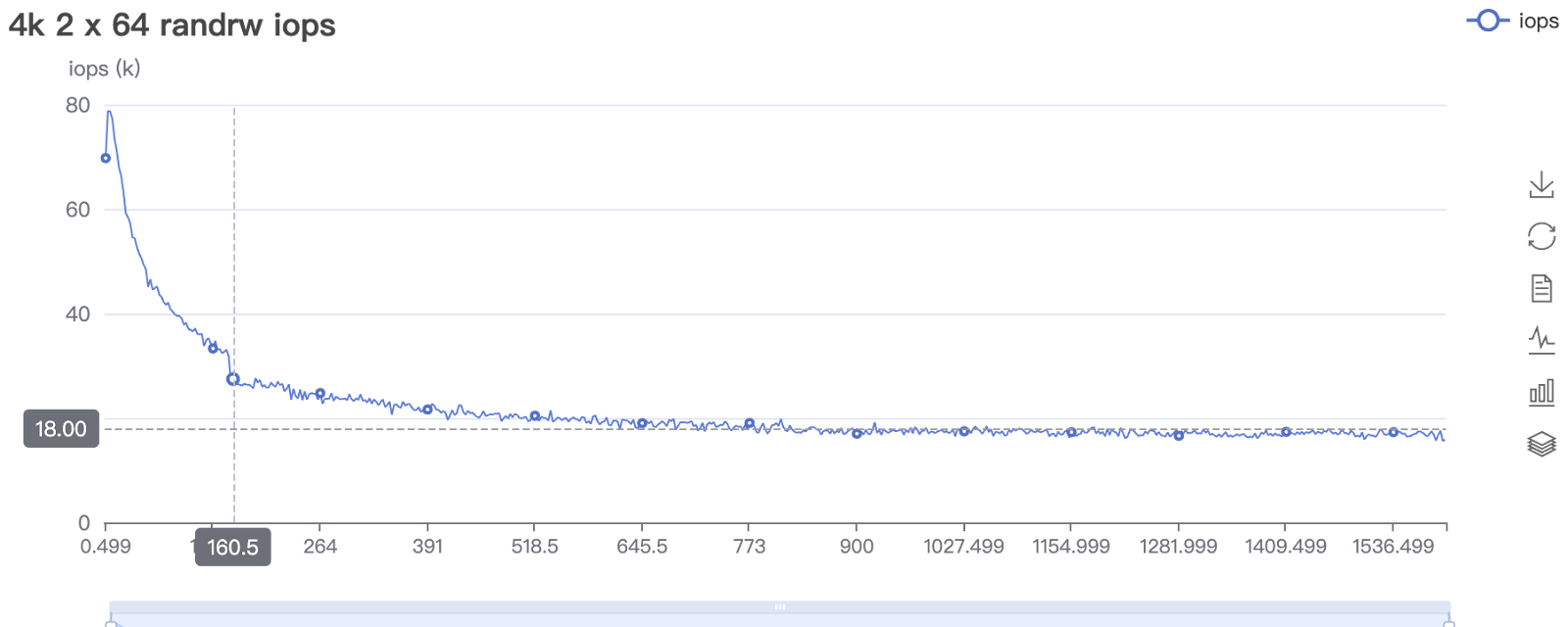
vSAN 8.0 OSA
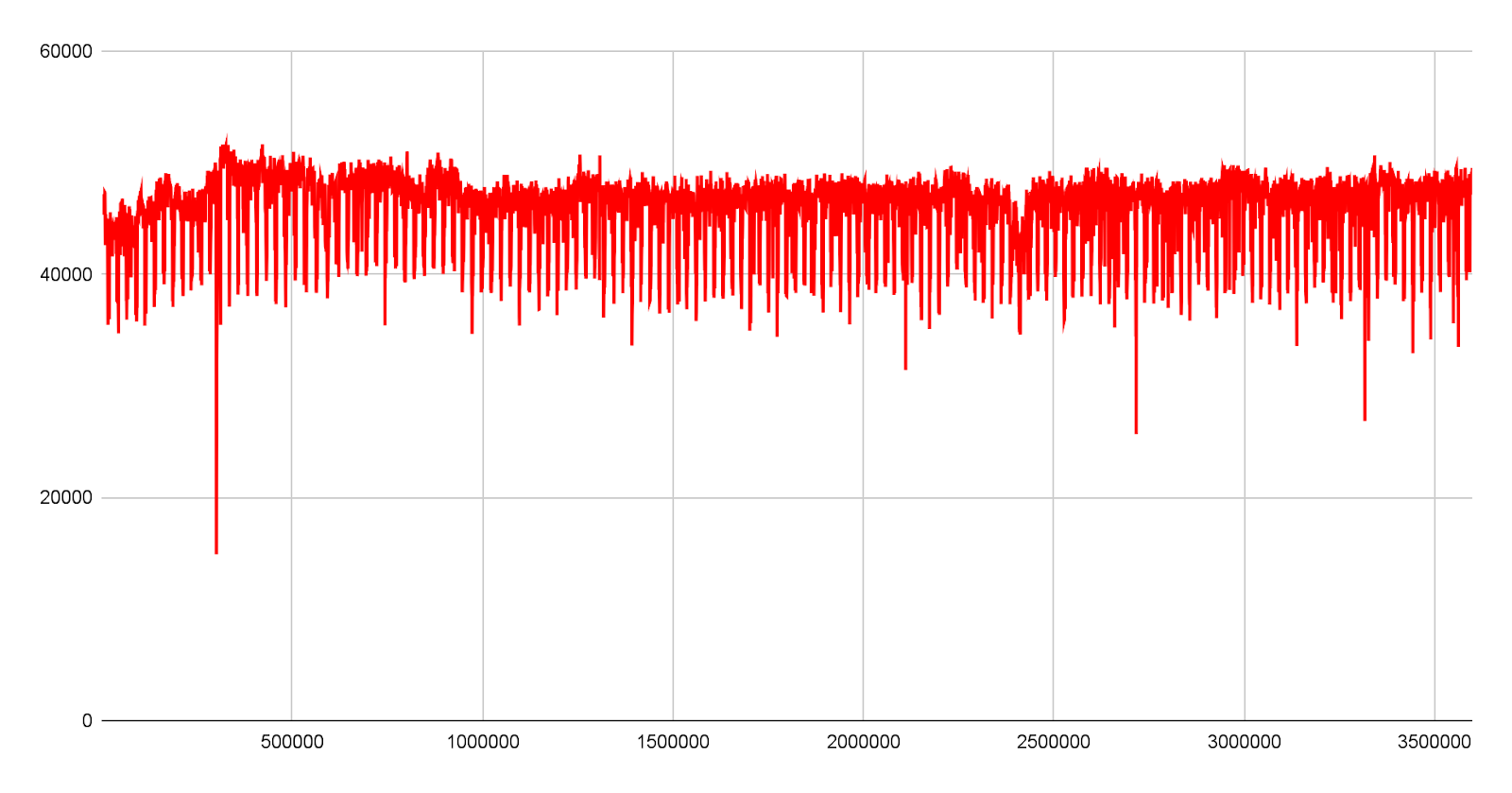
Long-term Performance and Stability Under Oracle Databases
In a 6-hour 3P3V 4K random write test under high-load conditions with storage utilization above 80%, Arcfra ACOS demonstrated superior and more stable performance.
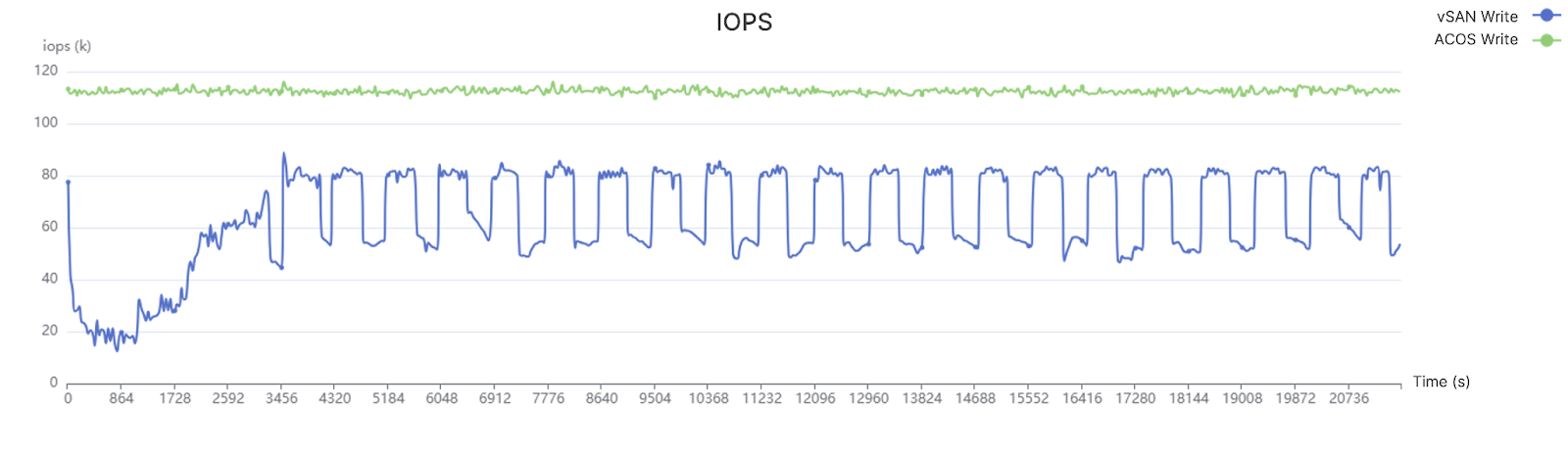
Green Curve: Arcfra ACOS Blue Curve:vSAN 8.0
Why Should You Replace VMware vSAN with Arcfra Distributed Storage?
Advantage #1 — Fully Comparable Storage Features
Arcfra ABS & AFS provide the same enterprise-grade reliability, performance, security, and other common features as VMware vSAN. With functions such as data checksum, data redundancy, rack topology awareness, and active-active-cluster support, ABS & AFS can offer different levels of data protection. When used together with Arcfra Backup & Disaster Recovery (ABDR), AECP can also achieve asynchronous replication of block storage data, thereby achieving production-grade high availability for the whole infra stack from local disks to cross-city clusters.
- ABS & AFS provide more flexible storage policies, with erasure coding (EC) configurations supporting fault-tolerance levels 1–4 and achieving more than 90% space utilization at maximum; they also support QoS control on volumes by IOPS or bandwidth, and allow I/O bursting.
- In addition to performing checksum verification on data, Arcfra ABS & AFS also conducts periodic automated data inspection to detect silent data corruption at an early stage and automatically restore data.
- Arcfra ABS & AFS not only perform health detection, alerting, and automated handling for disk issues, but also perform health detection, alerting, and handling for NICs and networks, providing comprehensive data protection.
- In hybrid-flash configurations or all-flash configurations with multiple types of SSDs, compared with vSAN OSA, Arcfra ABS & AFS stand out as they have no risk in cache disk single-point-of-failure. Their cache limit is also far higher than vSAN to avoid cache exhaustion, maintaining stable and superior performance under high space utilization. Plus, ABS & AFS also support online expansion of cache disks and capacity disks.
Advantage #2 — Fully Optimized Performance under Multiple Scenarios
With advanced features like volume pinning, I/O localization, and high-speed I/O access protocols, Arcfra distributed storage can meet the performance requirements of different applications while minimizing hardware investment. Performance tests in production environments show that Arcfra distributed storage outperforms VMware vSAN across various scenarios such as core business applications, databases, snapshots, and failure recovery.
- Arcfra distributed storage outperforms vSAN in multiple scenarios, including benchmark performance tests, long-term stress performance tests, post-snapshot performance tests, and failure-scenario performance tests. Although vSAN 8.0 introduces the ESA architecture and achieves improvements in space utilization and performance, the ESA architecture requires the use of all-NVMe SSDs, which results in higher hardware investment.
- In hybrid-flash configurations or all-flash configurations with multiple types of SSDs, Arcfra distributed storage uses volume pinning to ensure that data of certain volumes does not sink, thereby more flexibly meeting the performance requirements of different applications within a single cluster.
- When allocating data space, Arcfra distributed storage comprehensively considers factors such as local-prioritization, topology safety, and capacity balancing, and dynamically adjusts priorities under different utilization levels, achieving a balance between reliability and space utilization while providing optimal performance.
- Arcfra AFS allows clients to access the file system through each file controller. For clients with multi-point mounts and large numbers of concurrent read requests, access pressure can be distributed, providing faster response.
Advantage #3 — Flexible Supports for Two Virtualization Platforms
Arcfra distributed storage supports hyperconverged deployment with Arcfra Virtualization Engine (AVE) or VMware ESXi , meeting the needs of various application scenarios, while avoiding the high subscription costs of VMware VVF/VCF — As a built-in component of AECP, Arcfra distributed storage can be used without purchasing additional licenses.
For more information on Arcfra distributed storage features and VMware comparisons:
Arcfra vs. VMware: I/O Path Comparison and Performance Impact
Arcfra vs. VMware: VM Snapshot and I/O Performance Comparison
Arcfra Data Replication Explained: An Enhanced Strategy with Temporary Replica
High Availability, High Efficiency: Meet Arcfra File Storage
Arcfra Storage Tiering Model Explained
An In-Depth Look at Arcfra Erasure Coding: Configuration Strategies, Performance, and Best Practices
Download your go-to guide for navigating the post-VMware era for free: VMware Alternatives: Strategic Guide, Product Comparisons, and Customer Stories
Arcfra simplifies enterprise cloud infrastructure with a full-stack, software-defined platform built for the AI era. We deliver computing, storage, networking, security, Kubernetes, and more — all in one streamlined solution. Supporting VMs, containers, and AI workloads, Arcfra offers future-proof infrastructure trusted by enterprises across e-commerce, finance, and manufacturing. Arcfra is recognized by Gartner as a Representative Vendor in full-stack hyperconverged infrastructure. Learn more at www.arcfra.com.